Understanding BJT and FET Difference: A Simple Guide
When exploring the BJT and FET difference, it’s important to know what each type of transistor does. A BJT, or Bipolar Junction Transistor, is a type of transistor that controls current. On the other hand, an FET, or Field Effect Transistor, manages voltage. This basic difference can affect how they are used in electronic devices.
To help you understand the BJT and FET differences better, let’s break down their key features. BJTs are current-controlled and have three parts: the emitter, base, and collector. FETs are voltage-controlled and are simpler in their design. Knowing these differences can help you choose the right transistor for your electronic projects
What is a BJT and FET? Understanding the Basics of BJT and FET Difference
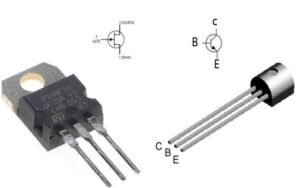
A BJT, or Bipolar Junction Transistor, is a type of transistor with three parts: the emitter, base, and collector. It controls electrical signals by using current. The BJT needs a current to operate, and it can amplify signals to make them stronger.
On the other hand, an FET, or Field Effect Transistor, works differently. It has three parts too: the source, gate, and drain. The FET controls electrical signals using voltage, not current. This means it only needs a small voltage to work, making it simpler and sometimes more efficient.
Both BJTs and FETs are important in electronics, but they are used in different ways. Understanding the BJT and FET difference helps you pick the right one for your project.
How BJT and FET Work: Key Differences in Function
The BJT controls signals by using current. When you apply current to the base, it changes how much current flows between the emitter and collector. This makes BJTs good for switching and amplifying signals.
FETs control signals using voltage. When you apply a voltage to the gate, it changes how much current flows between the source and drain. This makes FETs useful in circuits where you need to control voltage carefully.
Knowing how BJTs and FETs work helps in understanding the BJT and FET difference. Each type has its own strengths and is used in different kinds of circuits.
Current vs. Voltage: The Core BJT and FET Difference

The main BJT and FET difference is how they control electrical signals. BJTs are current-controlled devices. This means they need a current to operate and can amplify or switch signals based on that current.
In contrast, FETs are voltage-controlled devices. They need a small voltage to operate and can control larger currents. This difference in control method affects how each type of transistor is used in electronic devices.
Understanding whether you need a current-controlled or voltage-controlled device is crucial for choosing between a BJT and an FET.
BJT vs. FET: Which Transistor is Right for Your Project
Choosing between a BJT and an FET depends on what you need for your project. If you need to amplify signals or switch them on and off using current, a BJT might be the best choice. BJTs are great for these tasks because they respond well to changes in current.
If you need a transistor that works with voltage and is more efficient with power, then an FET might be better. FETs are often used in circuits where precision and efficiency are important.
Considering the BJT and FET difference can help you decide which transistor will work best for your electronic projects.
The Simple Differences Between BJT and FET Transistors
When you look at BJTs and FETs, you’ll see some simple differences. BJTs have three regions and are controlled by current. They are often used in amplifying signals and in switching applications.
FETs also have three parts but are controlled by voltage. They are usually more efficient and can be used in different types of circuits where voltage control is needed.
These straightforward differences make it easier to understand when to use each type of transistor based on your needs.
How BJT and FET Impact Electronic Devices: A Comparison
BJTs and FETs impact electronic devices in different ways. BJTs are often found in devices that need strong signal amplification. They are great at handling high currents and can switch signals effectively.
FETs, on the other hand, are used in devices where low power consumption and high efficiency are important. They are good for circuits that need precise control over voltage.
Comparing the BJT and FET difference helps in choosing the right transistor for specific applications in electronic devices.
Designing with BJTs and FETs: What You Need to Know About Their Differences
When designing with BJTs and FETs, it’s important to know their differences. BJTs require current to control the signal, so they are used in designs where current control is crucial.
FETs need voltage to control signals, making them suitable for designs that require low power and high efficiency. They are often used in modern electronic designs for better performance.
Understanding these design differences helps in creating circuits that work efficiently and meet specific needs.
BJT and FET in Action: Real-World Examples of Their Differences
In real-world applications, BJTs and FETs are used differently. For example, BJTs are commonly used in audio amplifiers and switching circuits where current control is important.
FETs are used in devices like computer processors and signal processing circuits where voltage control and efficiency are key. Seeing these real-world examples highlights the BJT and FET difference and helps in understanding their applications.
Conclusion
In summary, understanding the BJT and FET difference is important for picking the right transistor for your needs. BJTs are great for when you need to control and amplify current. They have three parts and work well in many electronic devices.
FETs, on the other hand, are better when you need to control voltage and be efficient with power. They also have three parts but operate differently. By knowing these differences, you can choose the best transistor for your projects and make your electronic designs work just right




